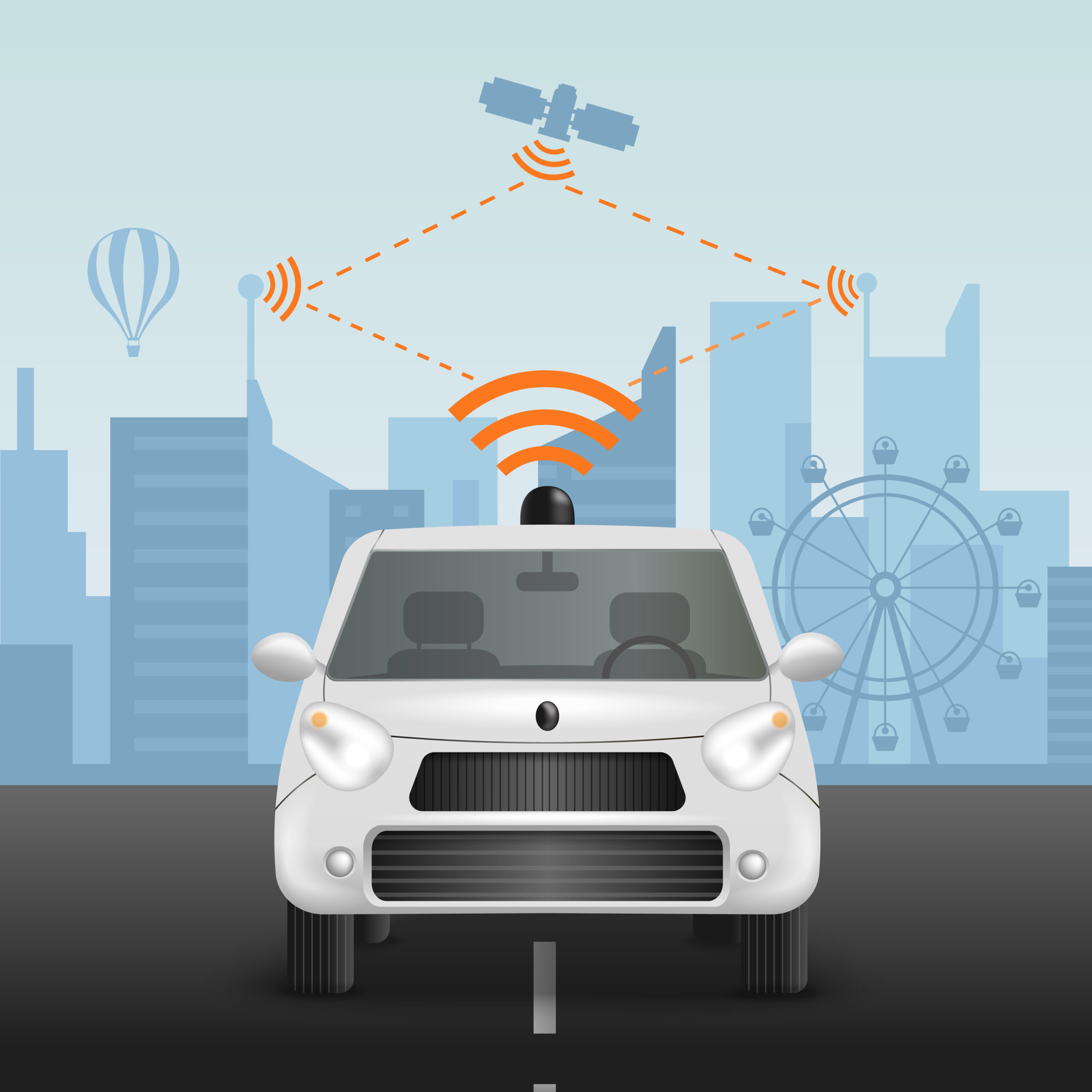
The world is on the brink of a transportation revolution with the advent of autonomous vehicles (AVs). These self-driving cars promise to transform how we commute, reduce traffic accidents, and enhance the efficiency of our transportation systems. As we navigate the rise of autonomous vehicles, it is essential to understand the latest developments and challenges shaping this groundbreaking technology.
Understanding Autonomous Vehicles
Autonomous vehicles, also known as self-driving cars or driverless cars, are equipped with advanced sensors, cameras, radar, and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate and drive without human intervention. These vehicles rely on a combination of hardware and software to perceive their environment, make decisions, and execute driving tasks.
Levels of Autonomy
The Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) has defined six levels of vehicle automation, ranging from Level 0 (no automation) to Level 5 (full automation):
- Level 0: No automation. The human driver is responsible for all driving tasks.
- Level 1: Driver assistance. The vehicle can assist with steering or acceleration/deceleration, but not both simultaneously.
- Level 2: Partial automation. The vehicle can control both steering and acceleration/deceleration, but the driver must remain engaged and monitor the driving environment.
- Level 3: Conditional automation. The vehicle can perform all driving tasks under certain conditions, but the driver must be ready to take control when needed.
- Level 4: High automation. The vehicle can perform all driving tasks in specific conditions or environments without human intervention.
- Level 5: Full automation. The vehicle can perform all driving tasks in all conditions without any human intervention.
Latest Developments in Autonomous Vehicles
The development of autonomous vehicles has accelerated rapidly, driven by advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technologies. Here are some of the latest developments in the field:
1. Enhanced Sensor Technologies
Modern autonomous vehicles are equipped with a variety of sensors, including LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), radar, cameras, and ultrasonic sensors. These sensors provide real-time data about the vehicle’s surroundings, enabling it to detect obstacles, pedestrians, and other vehicles. Recent advancements have improved the accuracy and reliability of these sensors, enhancing the overall safety and performance of AVs.
2. AI and Machine Learning
Artificial intelligence and machine learning play a crucial role in the functioning of autonomous vehicles. AI algorithms process data from the vehicle’s sensors to make real-time driving decisions. Machine learning models improve over time by learning from vast amounts of driving data. Companies like Tesla, Waymo, and Nvidia are at the forefront of developing sophisticated AI systems for self-driving cars.
3. 5G Connectivity
The rollout of 5G networks is set to revolutionize autonomous driving. 5G offers ultra-low latency and high-speed data transfer, enabling real-time communication between vehicles and infrastructure. This connectivity is essential for vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) and vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication, which enhances the safety and efficiency of autonomous vehicles.
4. Regulatory Developments
Governments and regulatory bodies worldwide are working to establish frameworks for the safe deployment of autonomous vehicles. The United States, European Union, China, and other countries have introduced regulations and guidelines to govern the testing and deployment of AVs. These regulations address safety standards, liability issues, and cybersecurity concerns.
5. Autonomous Ride-Hailing Services
Several companies are piloting autonomous ride-hailing services, offering a glimpse into the future of urban transportation. Waymo, a subsidiary of Alphabet Inc., operates a fully autonomous ride-hailing service in Phoenix, Arizona. Other companies like Uber and Lyft are also investing heavily in autonomous vehicle technology to launch their self-driving fleets.
6. Integration with Smart Cities
The concept of smart cities is closely linked with the development of autonomous vehicles. Smart cities leverage data and technology to improve urban living, and AVs play a critical role in this ecosystem. Autonomous vehicles can reduce traffic congestion, lower emissions, and improve mobility for residents. Cities like Singapore, Tokyo, and San Francisco are exploring ways to integrate AVs into their transportation networks.
Challenges Facing Autonomous Vehicles
Despite significant advancements, the widespread adoption of autonomous vehicles faces several challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the successful deployment and acceptance of AVs.
1. Safety Concerns
Safety is the paramount concern for autonomous vehicles. While AVs have the potential to reduce accidents caused by human error, ensuring the safety of these vehicles is complex. There have been high-profile accidents involving self-driving cars, raising questions about their reliability. Ensuring that AVs can safely navigate diverse driving conditions and respond to unexpected situations remains a significant challenge.
2. Regulatory and Legal Issues
The regulatory landscape for autonomous vehicles is still evolving. Different countries have varying regulations, making it challenging for companies to deploy AVs globally. Legal issues related to liability in case of accidents, insurance, and data privacy also need to be addressed. Establishing a consistent and comprehensive regulatory framework is essential for the widespread adoption of AVs.
3. Ethical and Moral Dilemmas
Autonomous vehicles must make split-second decisions that can have ethical and moral implications. For example, in a potential collision scenario, should the vehicle prioritize the safety of its passengers or pedestrians? These ethical dilemmas pose significant challenges for developers and policymakers. Ensuring that AVs make decisions aligned with societal values is a complex task.
4. Cybersecurity Threats
As connected devices, autonomous vehicles are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. Hackers could potentially take control of an AV, leading to catastrophic consequences. Ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to protect AVs from cyberattacks is crucial. This involves securing the vehicle’s software, communication networks, and data storage systems.
5. Public Acceptance
Gaining public trust and acceptance is vital for the success of autonomous vehicles. Many people are still skeptical about the safety and reliability of self-driving cars. Public education and awareness campaigns are necessary to address misconceptions and build confidence in AV technology. Demonstrating the benefits of AVs, such as increased safety and convenience, can help in gaining public acceptance.
6. Infrastructure Requirements
The deployment of autonomous vehicles requires significant infrastructure upgrades. This includes the development of smart roads, traffic signals, and communication networks to support V2V and V2X communication. Retrofitting existing infrastructure to accommodate AVs is a considerable challenge. Governments and city planners need to invest in infrastructure development to enable the seamless integration of AVs into the transportation system.
7. Economic and Job Implications
The rise of autonomous vehicles will have profound economic and job implications. While AVs have the potential to create new jobs in technology and maintenance, they may also displace jobs in driving and transportation sectors. Addressing the economic impact and providing support for workers affected by this transition is essential. Policymakers need to develop strategies to manage the economic disruption caused by the shift to autonomous vehicles.
The Future of Autonomous Vehicles
The future of autonomous vehicles is promising, but it requires overcoming significant challenges. Collaboration between technology companies, governments, and regulatory bodies is essential to address these challenges and pave the way for the widespread adoption of AVs.
Potential Benefits
The successful deployment of autonomous vehicles can bring numerous benefits:
- Improved Safety: By eliminating human error, AVs can significantly reduce traffic accidents and fatalities.
- Increased Efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can optimize routes, reduce traffic congestion, and improve fuel efficiency.
- Enhanced Mobility: AVs can provide mobility solutions for people with disabilities, the elderly, and those without access to traditional transportation.
- Environmental Impact: Autonomous vehicles can reduce emissions through optimized driving patterns and the adoption of electric and hybrid technologies.
- Economic Growth: The AV industry can drive economic growth by creating new jobs and business opportunities in technology, manufacturing, and services.
Collaboration and Innovation
The development of autonomous vehicles requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including technology companies, automotive manufacturers, governments, and research institutions. Continued innovation in AI, machine learning, sensor technologies, and connectivity is crucial to advancing AV technology.
Regulatory Harmonization
Harmonizing regulations across countries and regions is essential for the global deployment of autonomous vehicles. International cooperation can help establish consistent safety standards, liability frameworks, and data privacy protections. Regulatory bodies need to work together to create a conducive environment for the development and deployment of AVs.
Public Engagement
Engaging the public and addressing their concerns is vital for the acceptance of autonomous vehicles. Transparent communication about the benefits and risks of AVs can help build trust. Involving communities in the planning and implementation of AV projects can ensure that the technology meets their needs and expectations.
Ethical Frameworks
Developing ethical frameworks for autonomous vehicles is critical. These frameworks should guide decision-making processes in AVs, ensuring that they align with societal values and ethical principles. Policymakers, ethicists, and technologists need to collaborate to address the ethical dilemmas posed by autonomous driving.
Conclusion
The rise of autonomous vehicles marks a transformative period in transportation. While significant progress has been made, several challenges need to be addressed to realize the full potential of AVs. The latest developments in sensor technologies, AI, 5G connectivity, and regulatory frameworks are paving the way for safer and more efficient autonomous vehicles. However, safety concerns, regulatory and legal issues, ethical dilemmas, cybersecurity threats, public acceptance, infrastructure requirements, and economic implications must be carefully managed.
As we navigate the rise of autonomous vehicles, collaboration, innovation, and public engagement will be key to overcoming these challenges. The future of transportation is autonomous, and with the right strategies and frameworks, we can ensure that this future is safe, efficient, and beneficial for all.